一、反射机制
1.1、创建JavaBean类
package star.light.pojo;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
1.2、测试程序
package star.light.test;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class UserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 通过反射机制创建对象,假设已知要创建的类的属性名,且该类符合javabean规范
// 通过反射机制,获取类
String nameString = "name";
String ageString = "age";
Class classObject = Class.forName("star.light.pojo.User");
// 通过反射机制获取无参构造器,创建对象
Object object = classObject.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 通过反射机制,获取私有属性
Field usernameField = classObject.getDeclaredField(nameString);
Field ageField = classObject.getDeclaredField(ageString);
// 允许通过反射机制访问私有属性
usernameField.setAccessible(true);
// 设置私有属性的值
usernameField.set(object,"Sakura");
// 获取属性对象的set方法名
String setMethodName = "set" + ageString.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + ageString.substring(1);
// 通过反射机制,获取方法
Method setAgeMehtod = classObject.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName, ageField.getType());
// 通过反射机制,调用方法
setAgeMehtod.invoke(object, 10);
System.out.println(object);
}
}
二、Spring框架IOC的底层实现
2.1、引入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>star.light</groupId>
<artifactId>myspring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2.2、核心接口实现
package star.light.frame.core;
/**
* Spring框架应用上下文接口
*/
public interface ApplicationContext {
Object getBean(String beanName); // 根据bean的名称(id)获取相对应的bean对象
}
package star.light.frame.core;
import org.dom4j.*;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
private Map<String, Object> singletonObject = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 解析配置文件,初始化所有的bean对象
* @param configLocation 配置文件路径,配置文件应当放在类路径下
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) {
// 解析配置文件,然后实例化Bean,将Bean存放到singletonObject集合中
try {
// 这是dom4j解析XML文件的核心对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
// 获取一个输入流,指向配置文件
InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(configLocation);
// 读文件
Document document = reader.read(inputStream);
// 获取所有的bean标签
List<Node> beanNodes = document.selectNodes("//bean");
// 遍历bean标签
beanNodes.forEach(beanNode -> {
try {
// 向下转型,为了使用Element接口里更加丰富的方法
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
String id = beanElement.attributeValue("id");
String className = beanElement.attributeValue("class");
// 通过反射机制创建对象,将其放在Map集合中,提前曝光
Class classObject = Class.forName(className);
Object beanObject = classObject.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 将Bean曝光,加入Map集合
singletonObject.put(id,beanObject);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 再次重新把所有的bean标签遍历一次,这次主要给对象的属性赋值
beanNodes.forEach(beanNode -> {
try {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
// 获取id
String id = beanElement.attributeValue("id");
// 获取className
String className = beanElement.attributeValue("class");
// 获取类
Class classObject = Class.forName(className);
// 获取该bean标签下所有的属性标签
List<Element> properties = beanElement.elements("property");
// 遍历所有的属性标签
properties.forEach(property -> {
try {
// 获取属性名
String propertyName = property.attributeValue("name");
// 获取属性
Field field = classObject.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
// 获取set方法名
String setMethodName = "set" + propertyName.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + propertyName.substring(1);
// 获取set方法
Method setMethod = classObject.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName, field.getType());
// 获取具体的值
String value = property.attributeValue("value");
Object actualValue = null; // 真值
String ref = property.attributeValue("ref");
if (value != null) {
// 说明这个值是简单类型
// 调用set方法
// 这里只支持以下类型为简单类型
// byte、short、int、long、float、double、boolean、char
// Byte、Short、Integer、Long、Float、Double、Boolean、Character
// String
// 获取属性类型名
String propertyTypeSimpleName = field.getType().getSimpleName();
switch (propertyTypeSimpleName){
case "byte":
actualValue = Byte.parseByte(value);
break;
case "short":
actualValue = Short.parseShort(value);
break;
case "int":
actualValue = Integer.parseInt(value);
break;
case "long":
actualValue = Long.parseLong(value);
break;
case "float":
actualValue = Float.parseFloat(value);
break;
case "double":
actualValue = Double.parseDouble(value);
break;
case "boolean":
actualValue = Boolean.parseBoolean(value);
break;
case "char":
actualValue = value.charAt(0);
break;
case "Byte":
actualValue = Byte.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Short":
actualValue = Short.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Integer":
actualValue = Integer.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Long":
actualValue = Long.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Float":
actualValue = Float.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Double":
actualValue = Double.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Boolean":
actualValue = Boolean.valueOf(value);
break;
case "Character":
actualValue = Character.valueOf(value.charAt(0));
break;
case "String":
actualValue = value;
break;
}
setMethod.invoke(singletonObject.get(id),actualValue);
}
if (ref != null) {
// 说明这个值是非简单类型
// 调用set方法
setMethod.invoke(singletonObject.get(id),singletonObject.get(ref));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
return singletonObject.get(beanName);
}
}
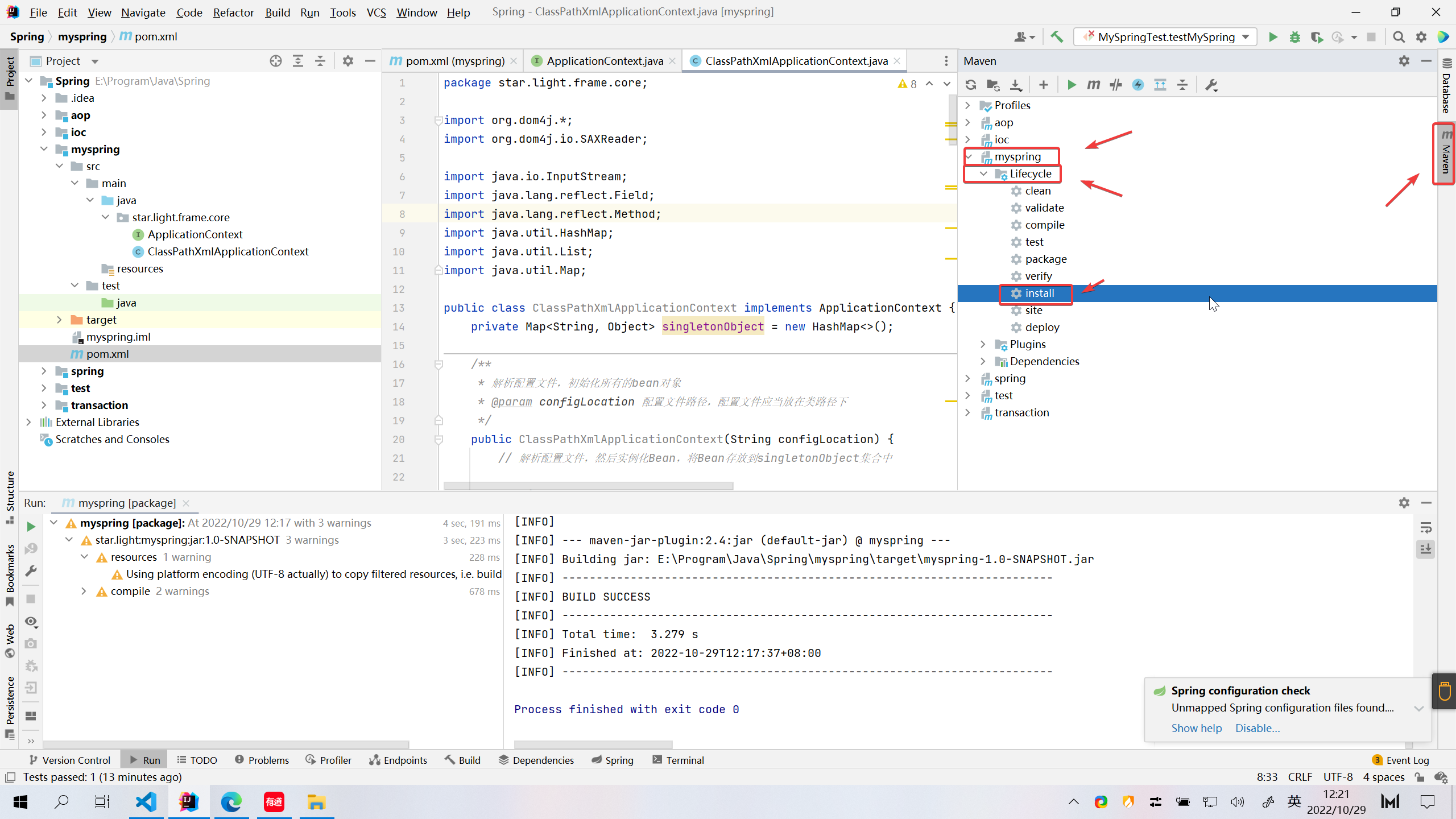
2.3、打包
三、框架的测试
3.1、引入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>star.light</groupId>
<artifactId>test</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入自己写的框架的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>star.light</groupId>
<artifactId>myspring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3.2、创建Bean类
package star.light.bean;
public class Wife {
private String name;
private Husband husband;
public Wife() {
}
public Wife(String name, Husband husband) {
this.name = name;
this.husband = husband;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Husband getHusband() {
return husband;
}
public void setHusband(Husband husband) {
this.husband = husband;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Wife{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", husband=" + husband.getName() +
'}';
}
}
package star.light.bean;
public class Husband {
private String name;
private Wife wife;
public Husband() {
}
public Husband(String name, Wife wife) {
this.name = name;
this.wife = wife;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Wife getWife() {
return wife;
}
public void setWife(Wife wife) {
this.wife = wife;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Husband{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", wife=" + wife.getName() +
'}';
}
}
3.3、创建核心配置文件
配置文件的取命随意,这里取命为 spring-config.xml,存放在类的根目录下;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="husband" class="star.light.bean.Husband">
<property name="name" value="李小狼"></property>
<property name="wife" ref="wife"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="wife" class="star.light.bean.Wife">
<property name="name" value="木之本樱"></property>
<property name="husband" ref="husband"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
3.4、测试程序
package star.light.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import star.light.frame.core.ApplicationContext;
import star.light.frame.core.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MySpringTest {
@Test
public void testMySpring(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
Object huaband = applicationContext.getBean("husband");
System.out.println(huaband);
Object wife = applicationContext.getBean("wife");
System.out.println(wife);
}
}
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/nanoha/p/16852118.html
1. 本站所有资源来源于用户上传和网络,如有侵权请邮件联系站长!
2. 分享目的仅供大家学习和交流,请务用于商业用途!
3. 如果你也有好源码或者教程,可以到用户中心发布,分享有积分奖励和额外收入!
4. 本站提供的源码、模板、插件等等其他资源,都不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
5. 如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系管理员处理!
6. 本站资源售价只是赞助,收取费用仅维持本站的日常运营所需!
7. 如遇到加密压缩包,默认解压密码为"gltf",如遇到无法解压的请联系管理员!
8. 因为资源和程序源码均为可复制品,所以不支持任何理由的退款兑现,请斟酌后支付下载
声明:如果标题没有注明"已测试"或者"测试可用"等字样的资源源码均未经过站长测试.特别注意没有标注的源码不保证任何可用性
