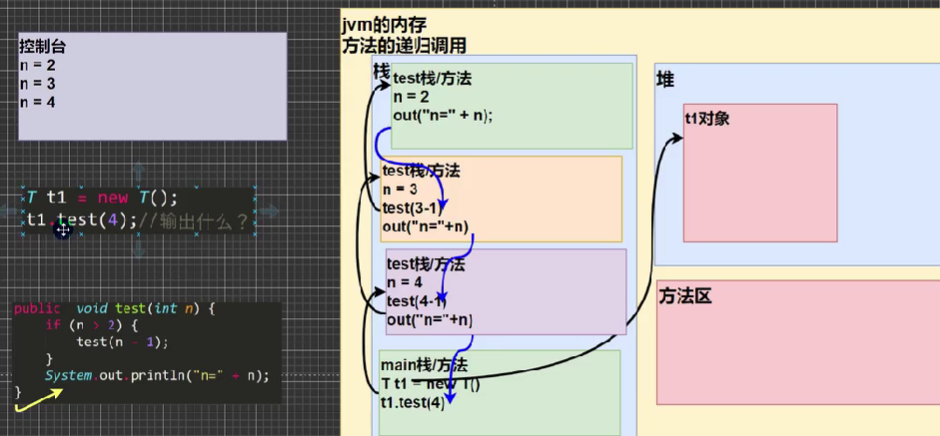
递归
递归:方法自己调用自己,每次调用时传入不同的变量
public class var{
public static void main(String[] args){
T t1 =new T();
t1.test(4);
}
}
class T{
public void test(int n){
if(n>2){
test(n-1);
}
System.out.println("n="+n);
}}//2,3,4
class T{
public void test(int n){
if(n>2){
test(n-1);
}else {System.out.println("n="+n);}
}}//2
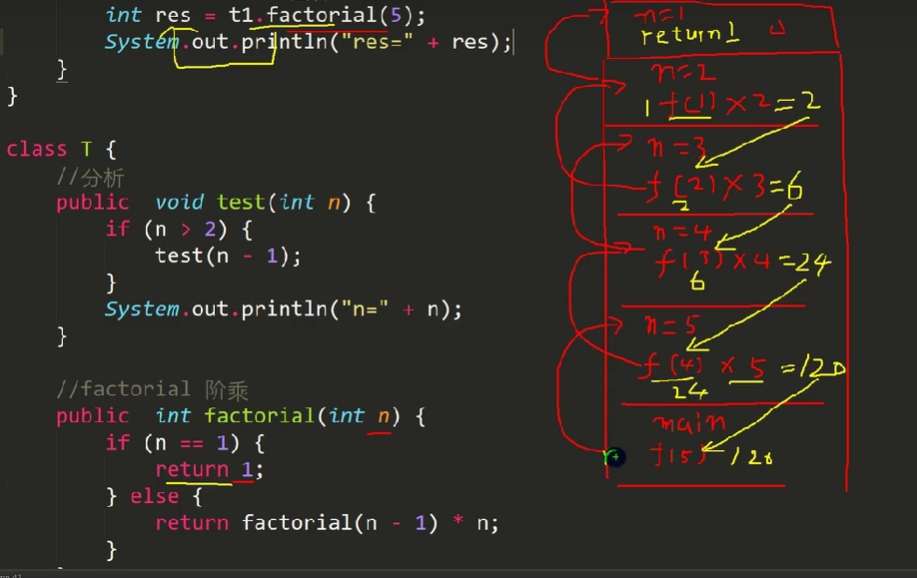
public class var{
public static void main(String[] args){
c t =new c();
int res =t.factorial(5);
System.out.println("res="+res);
}
}
class c{
public int factorial(int n){
if(n==1){
return 1;
}else{
return factorial(n-1)*n;
}
}
}

//使用递归的方式求出斐波那契数1,1,2,3,5,8,13..给你一个整数n,求出它的值
public class var{
public static void main(String[] args){
T t1=new T();
System.out.println("当n=7对应的数"+t1.fibonacci(7));
}
}
class T {
//1.当n=1,1;
//2.当n=2,1;n>=3,前面两个数之和
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n >= 1) {
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
} else {
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
} else {
System.out.println("要求输入大于1的整数");
return -1;
}
}
}
//猴子吃桃:有一堆桃子,猴子第一天吃了其中的一半,并再多吃了一个
//以后每天猴子都吃其中的一半,然后再多吃一个。当第10天时,想再吃发现只有一个桃子,问最开始有几个桃子
//规律 前一天的桃子=(后一天的桃子+1)*2
public class var{
public static void main(String[] args){
T t1=new T();
int day=1;
int peachNum=t1.peach(day);
if(peachNum!=-1){
System.out.println(peachNum);}
}
}
class T {
//1.当n=1,1;
//2.当n=2,1;n>=3,前面两个数之和
public int peach(int day){
if (day==10){
return 1;
}else if(day >=1 && day<=9){
return (peach(day+1)+1)*2;
}else{
System.out.println("输入天数范围错误");
return -1;}
}
}
小老鼠找迷宫
public class var {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.先创建迷宫,用二维数组表示 int[][] map=new int[8][7];
//2.先规定 map数组的元素值:0表示可以走的路,1表示障碍物
//3.将最上面的一行和最下面的一行全部设置为1
int[][] map = new int[8][7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<8;i++){
map[i][0]=1;
map[i][6]=1;}
map[3][1]=1;
map[3][2]=1;
//输出当前的地图
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
T t1=new T();
t1.findway(map,1,1);
System.out.println("找路的情况如下:");
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class T {
//使用递归回溯的思想
//如果找到了就返回true,否则返回false
// map二维数组即表示迷宫
//初始位置1,1;i,j就是老鼠的位置
//因为我们是递归找路,所以先规定map数组的各个值的含义
//0可以走;1障碍物;2可以走;3表示走过,但是走不通是死路
//6,5=2是终点,否则继续找
//先确定老鼠找路的策略 下-》右-》上-》左
public boolean findway(int[][] map, int i, int j) {
if (map[6][5] == 2) {
return true;
} else {
if (map[i][j] == 0) {
map[i][j] = 2;
//写策略
if (findway(map, i + 1, j)) {
return true;
} else if (findway(map, i, j + 1)) {
return true;
} else if (findway(map, i - 1, j)) {
return true;
} else if (findway(map, i, j - 1)) {
return true;
} else {
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
} else {//map[i][j]=1,2,3;
return false;
}
}
}
}
汉诺塔传说
public class var {
public static void main(String[] args) {
T tower = new T();
//tower.move(1,'A','B','C');
tower.move(2,'A','B','C');
}
}
class T {
//num表示要移动的个数,abc分别表示ABC塔
public void move(int num, char a, char b, char c) {
//如果只有一个盘num=1
if (num == 1) {
System.out.println(a + "->" + c);
} else {
//如果有多个盘,可以看成两个,最下面的和最上面的所有盘
//1.先移动上面所有的盘到b,借助c
move(num - 1, a, c, b);
//2.把最下面的盘移动到c
System.out.println(a + "->" + c);
//3.再把b塔的所有盘移动到c,借助a
move(num - 1, b, a, c);
}
}
}
3
编号为1的盘子正在从A移动到C
编号为2的盘子正在从A移动到B
编号为1的盘子正在从C移动到B
编号为3的盘子正在从A移动到C
编号为1的盘子正在从B移动到A
编号为2的盘子正在从B移动到C
编号为1的盘子正在从A移动到C
分析:num=3循环进入else;move(2,a,c,b);判断num=2进入循环,move(1,a,b,c)因为num=1跳出循环进入判断输出A->C
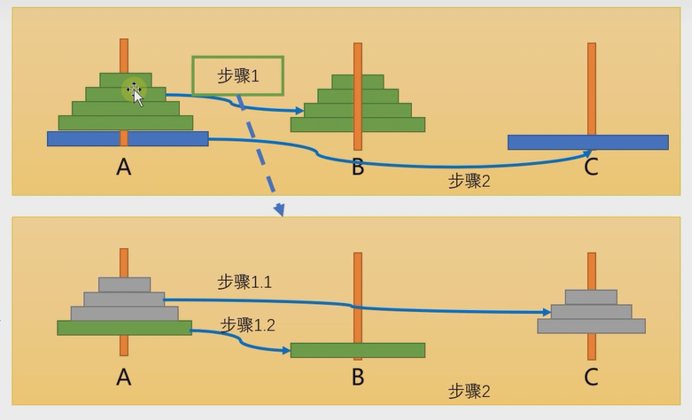
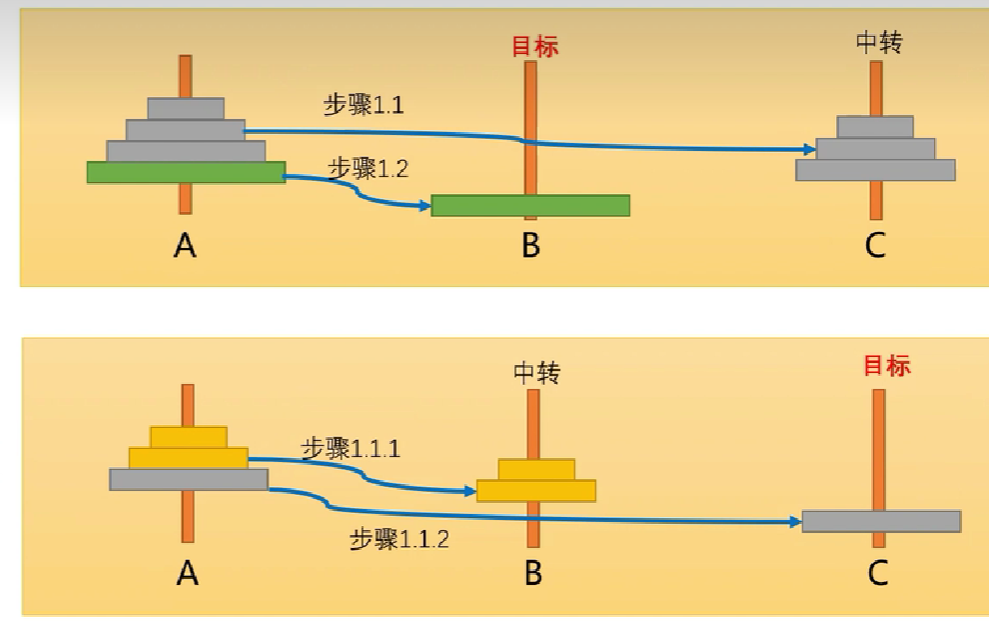

改进
public class var {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入盘数n:");
int n= sc.nextInt();
hanoi( n,'A','B','C');
}
/**
* 传入n个盘子,编号为1到n,按照汉诺r塔的规则,从目标A盘子移动到C,B是辅助盘子
* @param nDisks
* @param A
* @param B
* @param C
*/
public static void hanoi(int nDisks,char A,char B,char C){
if (nDisks==1){ //当只有一个盘子时,直接一步到位,把盘子从A移动到C
move(nDisks,A,C);
return;
}
hanoi(nDisks-1,A,C,B);//当n>=2时,步骤1,先把最上面的一大堆n-1个小盘子从A移动到B
move(nDisks,A,C);//步骤2,此时A上就剩下第你n个大盘子,只需要把它从A移动到C
hanoi(nDisks-1,B,A,C);//步骤3,此时需要将B上的n-1个小盘子从B移动到C
}
/**
* 将编号为n的盘子从starPoint移动到targetPoint
* @param nDisks
* @param sourceTower
* @param destTower
*/
private static void move(int nDisks,char sourceTower,char destTower) {
System.out.println("编号为"+nDisks+"的盘子正在从"+sourceTower+"移动到"+destTower);
}
}
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/maxzz/p/16837467.html
1. 本站所有资源来源于用户上传和网络,如有侵权请邮件联系站长!
2. 分享目的仅供大家学习和交流,请务用于商业用途!
3. 如果你也有好源码或者教程,可以到用户中心发布,分享有积分奖励和额外收入!
4. 本站提供的源码、模板、插件等等其他资源,都不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
5. 如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系管理员处理!
6. 本站资源售价只是赞助,收取费用仅维持本站的日常运营所需!
7. 如遇到加密压缩包,默认解压密码为"gltf",如遇到无法解压的请联系管理员!
8. 因为资源和程序源码均为可复制品,所以不支持任何理由的退款兑现,请斟酌后支付下载
声明:如果标题没有注明"已测试"或者"测试可用"等字样的资源源码均未经过站长测试.特别注意没有标注的源码不保证任何可用性
