条件控制
简单来说:当判断的条件为真时,执行某种代码逻辑,这就是条件控制。
那么在讲条件控制之前,可以给大家讲一个程序员当中流传的比较真实的一个例子
说有一天一个程序员,他的媳妇让他去出去买两个包子,那出去之前,他媳妇这么跟他说的,说老公你出去给我买两个包子
,如果看见卖西瓜的就买一个回来。
结果这个程序员回来了,买一个包子。结果媳妇给他一顿揍。
然后问他为啥,你为啥就买一个包子回来?,他回答他媳妇说我看见了卖西瓜的,所以买了一个包子。
其实这个就是条件控制一个典型的,一个生活化的一个说明场景
条件语句
条件控制就是我们常见的的if else
# y = |x|
if x < 0:
y = -x
else:
y = x
在条件语句后面加上 冒号:
python不支持switch语句,但是支持elif
if condition_1:
statement_1
elif condition_2:
statement_2
...
elif condition_i:
statement_i
else:
statement_n
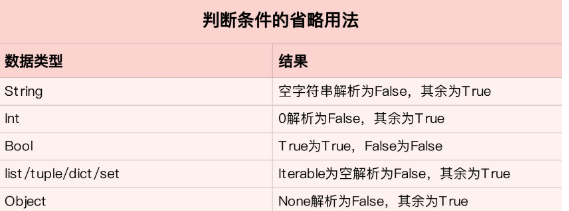
不少人喜欢省略半段的条件,就像这样
if s: # s is a string
...
if l: # l is a list
...
if i: # i is an int
...
...
循环语句
一般通过for循环和while循环实现
l = [1, 2, 3, 4]
for item in l:
print(item)
1
2
3
4
在python数据结构只要时可迭代对象,如列表,集合,等等,就可以遍历
for item in <iterable>:
...
但是字典本身只有键时课迭代的,如何要遍历字典的值和键值对,要通过内置的函数values() 和items() 实现
d = {'name': 'jason', 'dob': '2000-01-01', 'gender': 'male'}
for k in d: # 遍历字典的键
print(k)
name
dob
gender
for v in d.values(): # 遍历字典的值
print(v)
jason
2000-01-01
male
for k, v in d.items(): # 遍历字典的键值对
print('key: {}, value: {}'.format(k, v))
key: name, value: jason
key: dob, value: 2000-01-01
key: gender, value: male
当然可以通过索引来遍历元素
l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
for index in range(0, len(l)):
if index < 5:
print(l[index])
1
2
3
4
5
别忘了还有一个更重要的enumerate() 函数
l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
for index, item in enumerate(l):
if index < 5:
print(item)
1
2
3
4
5
在循环语句中,要通过continue 或break 一起使用
continue,就是让程序跳过当前这层循环,继续执行下面的循环
break 则是指完全跳出所在的整个循环体
现在找出价格小于1000,颜色不是红色的产品名称和颜色组合,如果不用continue
# name_price: 产品名称 (str) 到价格 (int) 的映射字典
# name_color: 产品名字 (str) 到颜色 (list of str) 的映射字典
for name, price in name_price.items():
if price < 1000:
if name in name_color:
for color in name_color[name]:
if color != 'red':
print('name: {}, color: {}'.format(name, color))
else:
print('name: {}, color: {}'.format(name, 'None'))
共用了5层for 或if 的嵌套
加上了continue,只有3层
# name_price: 产品名称 (str) 到价格 (int) 的映射字典
# name_color: 产品名字 (str) 到颜色 (list of str) 的映射字典
for name, price in name_price.items():
if price >= 1000:
continue
if name not in name_color:
print('name: {}, color: {}'.format(name, 'None'))
for color in name_color[name]:
if color == 'red':
continue
print('name: {}, color: {}'.format(name, color))
while
l = [1, 2, 3, 4]
index = 0
while index < len(l):
print(l[index])
index += 1
那么在什么场合使用for和continue
如果只是遍历已知的集合,找出满足条件的元素,使用for更加的简洁
如果需要在满足某个条件前,要不停的重复操作,并且没有特定的集合来遍历
例如
while True:
try:
text = input('Please enter your questions, enter "q" to exit')
if text == 'q':
print('Exit system')
break
...
...
print(response)
except as err:
print('Encountered error: {}'.format(err))
break
for 循环和while循环的效率问题
i = 0
while i < 1000000
i += 1
for i in range(0, 1000000):
pass
range()函数直接时C语言写的,调用的速度非常快,for循环的效率更高
对于有些大神直接写成一行操作
expression1 if condition else expression2 for item in iterable
分解成
for item in iterable:
if condition:
expression1
else:
expression2
如何没有else
expression for item in iterable if condition
现在绘制 y = 2*|x| + 5 的函数图像
只需一行
y = [value * 2 + 5 if x > 0 else -value * 2 + 5 for value in x]
在处理字符串时,将文件逐行读取,按照逗号分隔单词,去掉首位空字符,过滤小于3的单词,最后返回单词组成的列表
text = ' Today, is, Sunday'
text_list = [s.strip() for s in text.split(',') if len(s.strip()) > 3]
print(text_list)
['Today', 'Sunday']
给定两个列表 x、y,要求返回 x、y 中所有元素对组成的元组
[(xx, yy) for xx in x for yy in y if x != y]
l = []
for xx in x:
for yy in y:
if x != y:
l.append((x, y))
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/qlsh/p/16808286.html
